
Energy used in housing is one of the major sources of greenhouse gas emissions. We all can contribute by reducing our energy consumption. With more efficient windows and doors, you also reduce your heating or cooling costs, so the decision is a no brainer. That is why methods of lowering energy consumption and saving on heating costs are in high demand.

How do windows and doors contribute to the thermal insulation of a house or flat?
Good thermal insulation is only as effective as the weakest link in the chain. This is often, the old windows and entrance doors. The best masonry and wall insulations are of little use if you have inefficient doors and windows.
After long use, window and door frames often become warped and the seals lose their functionality. This allows cold air to flow freely into the rooms and warm air to escape.
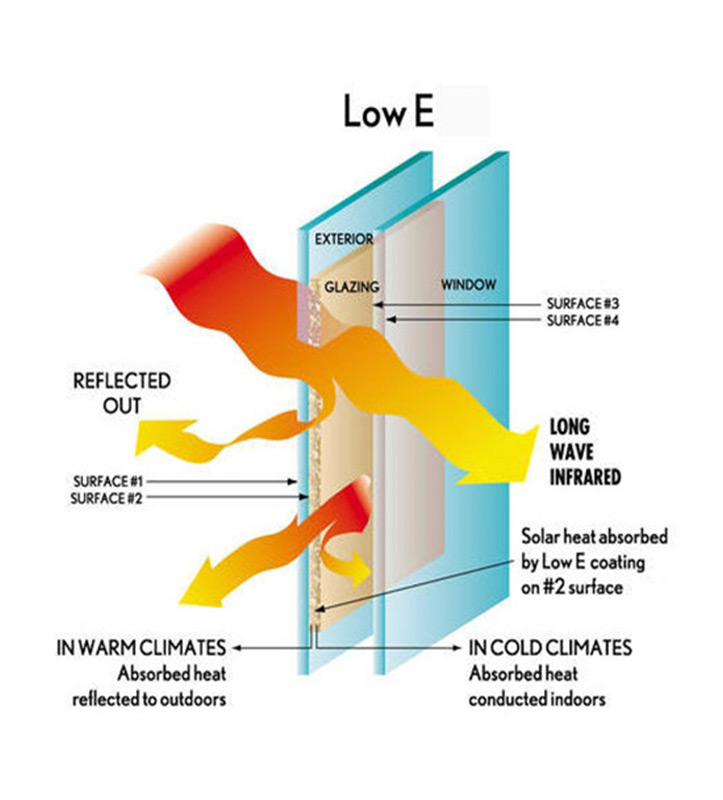
The ‘Uw value’ is often used to express energy efficiency. What does it stand for?
This value, which used to be called the ‘k-value’, is also known as the thermal transmittance and is given in watts per square metre Kelvin (W/m²K). It indicates the amount of heat that flows through 1 m² of a window at a constant temperature difference between the outside and the inside of the window of 1 Kelvin.
Simply expressed, the thermal transmittance Uw is made up of the thermal transmittance of the frame and sash profile (Uf), the glazing (Ug) and the glazing sealant compound used.
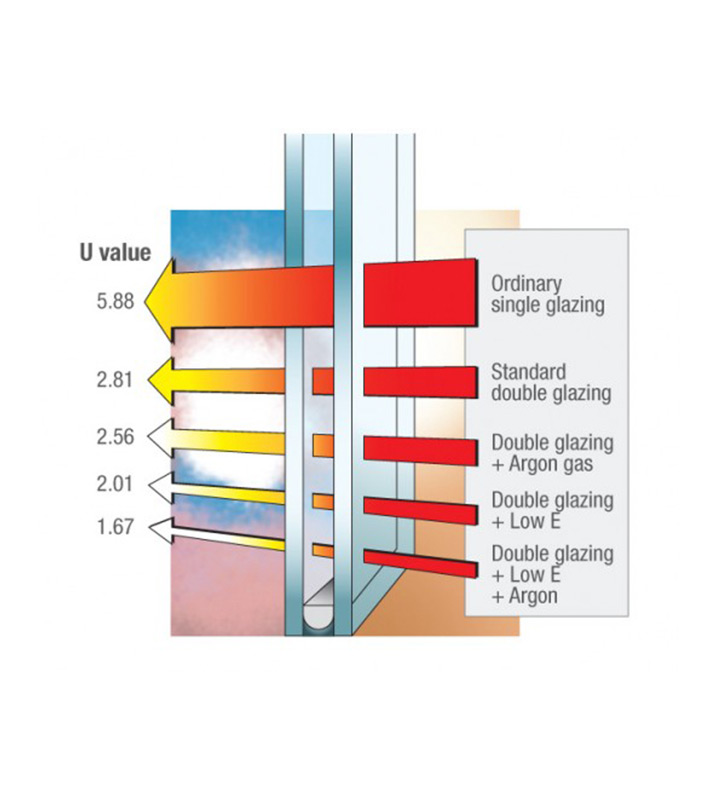
Less is more when it comes to the U value: the lower the Uw value, the better the window’s thermal insulation.
Rule of thumb:
For every 10% improvement in the Uw value you save about 1.2 litres of heating oil per square metre of window area per year.
Doesn’t sound like much? Let’s say you replace your windows from before 1995 (approx. Uw = 2.8 W/m²K) with new Aplast insulated windows (Uw = 1.0 W/m²K). For a single-family dwelling with a window area of approx. 30 m² this amounts to approx. 650 litres less heating oil!
With insulating glass from Aplast even the stringent requirements can easily be met. Decisive for this result are the glazing thermal protection measures, the space between the glass panes and the spacers in-between them. The insulating glass panes, coated with wafer-thin metal foils allow the short-wavelength rays of light in, but reflect the long-wavelength heat rays from the living space back inside.

Send your details and thoughts and ideas. We will be happy to get back to you!